Gertech Encoder Manufacturer - Rotary Incremental & Absolute Encoder Products Company
GERTECH is an technical enterprise Located in Weihai City ShanDong Province, China, has been providing Professional Industrial Automation Sensors Solutions for hundreds of enterprises all over the world since 2004. We offer the world’s broadest range of encoders for motion feedback control. For 17 years, Gertech have been providing innovative, customized system solutions for virtually any heavy-duty, industrial, servo- or light-duty application,and is committed to our people, customers and community and strives for excellence in safety, quality, delivery and customer service.
Gertech Manufactures and supplies safety systems for the door and gate market. The product portfolio includes optical and pneumatic sensing edges, bumpers, and photo-eye sensors which meet international standards for safety devices. These products have applications in commercial, bus, and train doors as well as production machines.
Our Main Products: A. Incremental Encoder; B. Programmable Incremental Encoder; C. Single-turn Absolute Encoder and multi-turn Absolute Encoder with Parallel, SSI, Modbus, Profibus, CANopen, Profinet, DeviceNet and EtherCAT interfaces; D. Draw Wire Encoder; E. Manual Pulse Generator; F. Optical Encoder Kit; G. Servo motor encoder;
Encoder with PROFINET interface has filled a gap in domestic market in China.
view moreCertificates
PRODUCTS
Our Main Products: Incremental Encoder, Absolute Encoder, Draw Wire Sensor, Manual Pluse Generator, Servo Motor Encoder etc.
- Incremental Encoder
- Absolute Encoder
- Draw Wire Sensor
- Manual Pluse Generator
- Servo Motor Encoder
-

GI-H60 Series 60mm Housing Hollow Shaft Incremental Encoder
▶Housing Diameter:60mm;
▶Bole Diameter:8,10,12,14,15mm;
▶Resolution: Max.6000ppr;
▶Supply Voltage:5v,8-29v;
▶Output Format: NPN/PNP open collector, Push pull, Line Driver;
▶Output Signal: A B / A B Z / A B Z & A- B- Z-; -

GIS-58 Series 58mm Housing Solid Shaft Incremental Encoder
▶Housing Diameter:38,50,58mm;
▶Solid/hollow Shaft Diameter:6,8,10mm;
▶Interface: Analog, 4-20mA, 0-10V;
▶Resolution: Single turn max.8192ppr;
▶Supply Voltage:5v,8-29v; -

GIS-MINI Series Mini Size 25mm,30mm Housing Solid Shaft Incremental Encoder
▶Housing Diameter:25,30mm;
▶Solid Shaft Diameter:4,5mm;
▶Resolution: Max.1024ppr;
▶Supply Voltage:5v,8-29v;
▶Output Format: NPN/PNP open collector, Push pull, Line Driver;
▶Output Signal: A B / A B Z / A B Z & A- B- Z-; -

GI-S50 Series 50mm Huosing Solid Shaft Incremental Encoder
▶GIS-40 Series Solid Shaft Incremental Rotary Encoder
▶Widely used in various fields of automatic control and measurement system,such as machinery manufacturing, shipping, textile, printing, aviation, military industry Testing machine, elevator, etc.
▶Vibration-resistant, corrosion-resistant, pollution-resistant;
-

GI-H100 Series 100mm Housing Hollow Shaft Incremental Encoder
▶Housing Diameter:100mm;
▶Bole Diameter:30,32,38,40,45mm;
▶Resolution: Max.6000ppr;
▶Supply Voltage:5v,8-29v;
▶Output Format: NPN/PNP open collector, Push pull, Line Driver;
▶Output Signal: A B / A B Z / A B Z & A- B- Z-; -

GI-H40 Series 40mm Housing Hollow Shaft Incremental Encoder
▶Housing Diameter:38mm;
▶Hollow Shaft Diameter:6,8mm;
▶Resolution: Max.6000ppr;
▶Supply Voltage:5v,8-29v;
▶Output Format: NPN/PNP open collector, Push pull, Line Driver;
▶Output Signal: A B / A B Z / A B Z & A- B- Z-; -

GI-S40 Series 40mm Housing Solid Shaft Incremental Encoder
▶ Housing Diameter:38mm;
▶ Solid Shaft Diameter:6mm;
▶ Resolution: Max.10000ppr;
▶ Supply Voltage:5v,8-29v;
▶ Output Format: NPN/PNP open collector, Push pull, Line Driver;
▶ Output Signal: A B / A B Z / A B Z & A- B- Z-; -

GI-HK Series Optical Encoder Kit Housing Diameter:30mm; Solid/hollow Shaft Diameter:3-10mm;
▶Housing Diameter:30mm;
▶Shaft Diameter:3-10mm;
▶Resolution: Max.1000ppr;
▶Supply Voltage:5v,8-29v;
▶Output Format: Voltage Output, Differential Output
▶Output Signal: A B / A B Z; -

GI-H90 Series 90mm Housing Hollow Shaft Incremental Encoder
▶Housing Diameter:90mm;
▶Bole Diameter:20,30,32,38,40mm;
▶Resolution: Max.6000ppr;
▶Supply Voltage:5v,8-29v;
▶Output Format: NPN/PNP open collector, Push pull, Line Driver;
▶Output Signal: A B / A B Z / A B Z & A- B- Z-; -

GI-H80 Series 80mm Housing Hollow Shaft Incremental Encoder
▶Housing Diameter:80mm;
▶Bole Diameter:18,20,30mm;
▶Resolution: Max.6000ppr;
▶Supply Voltage:5v,8-29v;
▶Output Format: NPN/PNP open collector, Push pull, Line Driver;
▶Output Signal: A B / A B Z / A B Z & A- B- Z-; -

GI-H60 Series 60mm Housing Hollow Shaft Incremental Encoder
▶Housing Diameter:60mm;
▶Bole Diameter:8,10,12,14,15mm;
▶Resolution: Max.6000ppr;
▶Supply Voltage:5v,8-29v;
▶Output Format: NPN/PNP open collector, Push pull, Line Driver;
▶Output Signal: A B / A B Z / A B Z & A- B- Z-; -

GIS-58 Series 58mm Housing Solid Shaft Incremental Encoder
▶Housing Diameter:38,50,58mm;
▶Solid/hollow Shaft Diameter:6,8,10mm;
▶Interface: Analog, 4-20mA, 0-10V;
▶Resolution: Single turn max.8192ppr;
▶Supply Voltage:5v,8-29v; -

GIS-MINI Series Mini Size 25mm,30mm Housing Solid Shaft Incremental Encoder
▶Housing Diameter:25,30mm;
▶Solid Shaft Diameter:4,5mm;
▶Resolution: Max.1024ppr;
▶Supply Voltage:5v,8-29v;
▶Output Format: NPN/PNP open collector, Push pull, Line Driver;
▶Output Signal: A B / A B Z / A B Z & A- B- Z-; -

GI-S50 Series 50mm Huosing Solid Shaft Incremental Encoder
▶GIS-40 Series Solid Shaft Incremental Rotary Encoder
▶Widely used in various fields of automatic control and measurement system,such as machinery manufacturing, shipping, textile, printing, aviation, military industry Testing machine, elevator, etc.
▶Vibration-resistant, corrosion-resistant, pollution-resistant;
-

GI-H100 Series 100mm Housing Hollow Shaft Incremental Encoder
▶Housing Diameter:100mm;
▶Bole Diameter:30,32,38,40,45mm;
▶Resolution: Max.6000ppr;
▶Supply Voltage:5v,8-29v;
▶Output Format: NPN/PNP open collector, Push pull, Line Driver;
▶Output Signal: A B / A B Z / A B Z & A- B- Z-; -

GI-H40 Series 40mm Housing Hollow Shaft Incremental Encoder
▶Housing Diameter:38mm;
▶Hollow Shaft Diameter:6,8mm;
▶Resolution: Max.6000ppr;
▶Supply Voltage:5v,8-29v;
▶Output Format: NPN/PNP open collector, Push pull, Line Driver;
▶Output Signal: A B / A B Z / A B Z & A- B- Z-; -

GI-S40 Series 40mm Housing Solid Shaft Incremental Encoder
▶ Housing Diameter:38mm;
▶ Solid Shaft Diameter:6mm;
▶ Resolution: Max.10000ppr;
▶ Supply Voltage:5v,8-29v;
▶ Output Format: NPN/PNP open collector, Push pull, Line Driver;
▶ Output Signal: A B / A B Z / A B Z & A- B- Z-; -

GI-HK Series Optical Encoder Kit Housing Diameter:30mm; Solid/hollow Shaft Diameter:3-10mm;
▶Housing Diameter:30mm;
▶Shaft Diameter:3-10mm;
▶Resolution: Max.1000ppr;
▶Supply Voltage:5v,8-29v;
▶Output Format: Voltage Output, Differential Output
▶Output Signal: A B / A B Z;
-

GSA-S Series Single-Turn SSI Absolute Rotary Encoder
▶Housing Diameter:38,50,58mm;
▶Solid/hollow Shaft Diameter:6,8,10mm;
▶Interface: SSI;
▶Resolution: Single turn max.16bits;
▶Supply Voltage:5v,8-29v;
▶Output Code: Binary, Gray, Gray Excess, BCD; -

GSA-B Series Single-Turn Biss Absolute Rotary Encoder
▶Housing Diameter:38,50,58mm;
▶Solid/hollow Shaft Diameter:6,8,10mm;
▶Interface: BISS;
▶Resolution: Single turn max.1024ppr/max.2048ppr;
▶Supply Voltage:5v,8-29v;
▶Output Code: Binary, Gray, Gray Excess,BCD ; -

GSA-PL Series, Single Turn Parallel Absolute Encoder
▶Housing Diameter:38,50,58mm;
▶Solid/hollow Shaft Diameter:6,8,10mm;
▶Interface: Parallel;
▶Resolution: Max.16bits;
▶Supply Voltage:5v,8-29v;
▶Output Code: Binary, Gray, Gray Excess, BCD; -

GMA-C Series CANopen Interface Bus-based Multi-turn Absolute Encoder
▶Housing Diameter:58mm;
▶Hollow Shaft Diameter:12mm;
▶Resolution: Turns: Single Turn:Max.16bit;
▶CANopen Interface;
▶Supply Voltage: 8-30v; -

GMA-C Series CANopen Interface Bus-based Multi-turn Absolute Encoder
▶Housing Diameter:58mm;
▶Hollow Shaft Diameter:12mm;
▶Resolution: Max.16bits Turns: Single Turn:Max.16bit; total max29bits
▶CANopen Interface;
▶Supply Voltage: 8-30v; -

GMA-PN Series Profinet Interface Ethernet Multi-turn Absolute Encoder
▶Housing Diameter:58mm;
▶Solid/hollow Shaft Diameter:10mm;
▶Output: Profinet;
▶Resolution: Multi-turn Max.12bits turns, Single Turn Max.13bits;
▶Supply Voltage:5v,8-29v; -

GMA-DP Series Profibus-DP Interface Bus-based Absolute Encoder
▶Housing Diameter:58mm;
▶Solid/hollow Shaft Diameter:10mm;
▶Output: Profibus-DP;
▶Resolution: Multi-turn Max.12bits turns, Single Turn Max.13bits;
▶Supply Voltage:5v,8-29v; -

GSA-A Series Single-Turn Analog Absolute Rotary Encoder
▶Housing Diameter:38,50,58mm;
▶Solid/hollow Shaft Diameter:6,8,10mm;
▶Interface: Analog, 4-20mA, 0-10V;
▶Resolution: Single turn max.8192ppr;
▶Supply Voltage:5v,8-29v; -

GSA-C Series CANopen Single Turn Bus-based Absolute Encoder
▶Housing Diameter:58mm;
▶Hollow Shaft Diameter:12mm;
▶Resolution: Single Turn:Max.16bit;
▶CANopen Interface;
▶Supply Voltage: 8-30v; -

GSA-M Series Single Turn Modbus Absolute Encoder
▶Housing Diameter:38,50,58mm;
▶Solid/hollow Shaft Diameter:6,8,10mm;
▶Interface: Modbus;
▶Resolution: Single turn max.16bits;
▶Supply Voltage:5v,8-29v;
▶Output Code: Binary, Gray, Gray Excess, BCD; -

GSA-S Series Single-Turn SSI Absolute Rotary Encoder
▶Housing Diameter:38,50,58mm;
▶Solid/hollow Shaft Diameter:6,8,10mm;
▶Interface: SSI;
▶Resolution: Single turn max.16bits;
▶Supply Voltage:5v,8-29v;
▶Output Code: Binary, Gray, Gray Excess, BCD; -

GSA-B Series Single-Turn Biss Absolute Rotary Encoder
▶Housing Diameter:38,50,58mm;
▶Solid/hollow Shaft Diameter:6,8,10mm;
▶Interface: BISS;
▶Resolution: Single turn max.1024ppr/max.2048ppr;
▶Supply Voltage:5v,8-29v;
▶Output Code: Binary, Gray, Gray Excess,BCD ; -

GSA-PL Series, Single Turn Parallel Absolute Encoder
▶Housing Diameter:38,50,58mm;
▶Solid/hollow Shaft Diameter:6,8,10mm;
▶Interface: Parallel;
▶Resolution: Max.16bits;
▶Supply Voltage:5v,8-29v;
▶Output Code: Binary, Gray, Gray Excess, BCD; -

GMA-C Series CANopen Interface Bus-based Multi-turn Absolute Encoder
▶Housing Diameter:58mm;
▶Hollow Shaft Diameter:12mm;
▶Resolution: Turns: Single Turn:Max.16bit;
▶CANopen Interface;
▶Supply Voltage: 8-30v; -

GMA-C Series CANopen Interface Bus-based Multi-turn Absolute Encoder
▶Housing Diameter:58mm;
▶Hollow Shaft Diameter:12mm;
▶Resolution: Max.16bits Turns: Single Turn:Max.16bit; total max29bits
▶CANopen Interface;
▶Supply Voltage: 8-30v; -

GMA-PN Series Profinet Interface Ethernet Multi-turn Absolute Encoder
▶Housing Diameter:58mm;
▶Solid/hollow Shaft Diameter:10mm;
▶Output: Profinet;
▶Resolution: Multi-turn Max.12bits turns, Single Turn Max.13bits;
▶Supply Voltage:5v,8-29v; -

GMA-DP Series Profibus-DP Interface Bus-based Absolute Encoder
▶Housing Diameter:58mm;
▶Solid/hollow Shaft Diameter:10mm;
▶Output: Profibus-DP;
▶Resolution: Multi-turn Max.12bits turns, Single Turn Max.13bits;
▶Supply Voltage:5v,8-29v; -

GSA-A Series Single-Turn Analog Absolute Rotary Encoder
▶Housing Diameter:38,50,58mm;
▶Solid/hollow Shaft Diameter:6,8,10mm;
▶Interface: Analog, 4-20mA, 0-10V;
▶Resolution: Single turn max.8192ppr;
▶Supply Voltage:5v,8-29v;
-

GI-D333 Series 0-20000mm Measurement Range Draw Wire Encoder
▶Size:120mm x 58.5mm;
▶Measurement Range: 0-20000mm;
▶Supply Voltage:5v,8-29v;
▶Output Format: Analog-0-10v, 4-20mA;
▶Incremental:NPN/PNP open collector, Push pull, Line Driver;
▶Absolute:Biss, SSI, Modbus, CANopen, Profibus-DP, Profinet, EtherCAT, Parallel etc -

GI-D200 Series 0-15000/20000mm Measurement Range Draw Wire Encoder
▶Size: 252mm x 252mm x 190mm/300mm x 300mm x 220mm;
▶Measurement Range: 0-15000/20000mm;
▶Supply Voltage:5v,8-29v;
▶Output Format: Analog-0-10v, 4-20mA;
▶Incremental:NPN/PNP open collector, Push pull, Line Driver;
▶Absolute:Biss, SSI, Modbus, CANopen, Profibus-DP, Profinet, EtherCAT, Parallel etc. -

GI-D315 Series 0-10000mm Measurement Range Draw Wire Encoder
▶Size:120mm x 120mm x 246mm;
▶Measurement Range: 0-10000mm;
▶Supply Voltage:5v,8-29v;
▶Output Format: Analog-0-10v, 4-20mA;
▶Incremental:NPN/PNP open collector, Push pull, Line Driver;
▶Absolute:Biss, SSI, Modbus, CANopen, Profibus-DP, Profinet, EtherCAT, Parallel etc -

GI-D15 Series 0-500mm Measurement Range Draw Wire Encoder
▶Size:30 x 30mm Hub:40/50mm
▶Measurement Range: 0-500mm;
▶Supply Voltage:5v,24v,5-24v;
▶Output Format: Analog-0-10v, 4-20mA; -

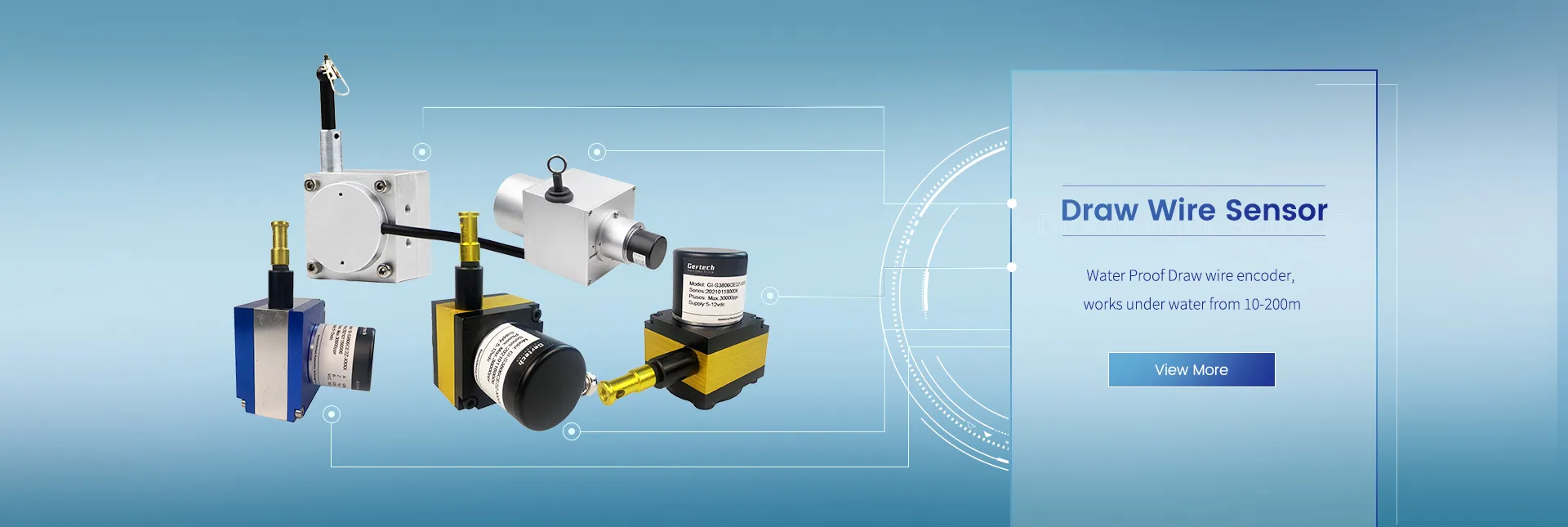
GI-WF Series Water Proof Draw Wire Sensors Using 0-200m in the water
▶Water Proof Draw wire encoder, works under water from 10-200m, for more details plz feel free to contact;
-

GI-D20 Series 0-1200mm Measurement Range Draw Wire Sensor
▶Size:50x50x76mm;
▶Measurement Range: 0-1200mm;
▶Supply Voltage:5v,8-29v,24v;
▶Output Format: Analog-0-10v, 4-20mA;
▶Incremental:NPN/PNP open collector, Push pull, Line Driver;
▶Absolute:Biss, SSI, Modbus, CANopen, Profibus-DP, Profinet, EtherCAT, Parallel etc. -

GI-D50 Series 0-2000mm Measurement Range Draw Wire Encoder
▶Size:63x63x78mm;
▶Measurement Range: 0-2000mm;
▶Supply Voltage:24v;
▶Output Format: Analog-0-10v, 4-20mA;
▶Incremental:NPN/PNP open collector, Push pull, Line Driver;
Absolute:Biss, SSI, Modbus, CANopen, Profibus-DP, Profinet, EtherCAT, Parallel etc. -

GI-D100 Series 0-7000mm Measurement Range Draw Wire Encoder
▶Size: 130x130x95mm;
▶Measurement Range: 0-7000mm;
▶Supply Voltage:5v,8-29v;
▶Output Format: Analog-0-10v, 4-20mA;
▶Incremental:NPN/PNP open collector, Push pull, Line Driver;
▶Absolute:Biss, SSI, Modbus, CANopen, Profibus-DP, Profinet, EtherCAT, Parallel etc. -

GI-D120 Series 0-10000mm Measurement Range Draw Wire Encoder
▶Size: 252mm x 252mm x 190mm/300mm x 300mm x 220mm;
▶Measurement Range: 0-15000/20000mm;
▶Supply Voltage:5v,8-29v;
▶Output Format: Analog-0-10v, 4-20mA;
▶Incremental:NPN/PNP open collector, Push pull, Line Driver;
▶Absolute:Biss, SSI, Modbus, CANopen, Profibus-DP, Profinet, EtherCAT, Parallel etc. -

GI-D333 Series 0-20000mm Measurement Range Draw Wire Encoder
▶Size:120mm x 58.5mm;
▶Measurement Range: 0-20000mm;
▶Supply Voltage:5v,8-29v;
▶Output Format: Analog-0-10v, 4-20mA;
▶Incremental:NPN/PNP open collector, Push pull, Line Driver;
▶Absolute:Biss, SSI, Modbus, CANopen, Profibus-DP, Profinet, EtherCAT, Parallel etc -

GI-D200 Series 0-15000/20000mm Measurement Range Draw Wire Encoder
▶Size: 252mm x 252mm x 190mm/300mm x 300mm x 220mm;
▶Measurement Range: 0-15000/20000mm;
▶Supply Voltage:5v,8-29v;
▶Output Format: Analog-0-10v, 4-20mA;
▶Incremental:NPN/PNP open collector, Push pull, Line Driver;
▶Absolute:Biss, SSI, Modbus, CANopen, Profibus-DP, Profinet, EtherCAT, Parallel etc. -

GI-D315 Series 0-10000mm Measurement Range Draw Wire Encoder
▶Size:120mm x 120mm x 246mm;
▶Measurement Range: 0-10000mm;
▶Supply Voltage:5v,8-29v;
▶Output Format: Analog-0-10v, 4-20mA;
▶Incremental:NPN/PNP open collector, Push pull, Line Driver;
▶Absolute:Biss, SSI, Modbus, CANopen, Profibus-DP, Profinet, EtherCAT, Parallel etc -

GI-D15 Series 0-500mm Measurement Range Draw Wire Encoder
▶Size:30 x 30mm Hub:40/50mm
▶Measurement Range: 0-500mm;
▶Supply Voltage:5v,24v,5-24v;
▶Output Format: Analog-0-10v, 4-20mA; -

GI-WF Series Water Proof Draw Wire Sensors Using 0-200m in the water
▶Water Proof Draw wire encoder, works under water from 10-200m, for more details plz feel free to contact;
-

GI-D20 Series 0-1200mm Measurement Range Draw Wire Sensor
▶Size:50x50x76mm;
▶Measurement Range: 0-1200mm;
▶Supply Voltage:5v,8-29v,24v;
▶Output Format: Analog-0-10v, 4-20mA;
▶Incremental:NPN/PNP open collector, Push pull, Line Driver;
▶Absolute:Biss, SSI, Modbus, CANopen, Profibus-DP, Profinet, EtherCAT, Parallel etc. -

GI-D50 Series 0-2000mm Measurement Range Draw Wire Encoder
▶Size:63x63x78mm;
▶Measurement Range: 0-2000mm;
▶Supply Voltage:24v;
▶Output Format: Analog-0-10v, 4-20mA;
▶Incremental:NPN/PNP open collector, Push pull, Line Driver;
Absolute:Biss, SSI, Modbus, CANopen, Profibus-DP, Profinet, EtherCAT, Parallel etc. -

GI-D100 Series 0-7000mm Measurement Range Draw Wire Encoder
▶Size: 130x130x95mm;
▶Measurement Range: 0-7000mm;
▶Supply Voltage:5v,8-29v;
▶Output Format: Analog-0-10v, 4-20mA;
▶Incremental:NPN/PNP open collector, Push pull, Line Driver;
▶Absolute:Biss, SSI, Modbus, CANopen, Profibus-DP, Profinet, EtherCAT, Parallel etc.
-

GT-1468 Series Manual Pluse Generator With Emergency Stop Button For CNC Lathe And Printing Mechanis
▶Size:134*68mm;
▶Resolution:20ppr,100ppr;
▶Supply Voltage:5v, 12v, 5-24v(+-10%)
▶Output form:Line Driver, Voltage Output
▶Emergency Button:Yes
▶Enable Button:Yes -

GT-1469 Series Manual Pluse Generator For CNC Lathe And Printing Mechanism
▶Size:134*68mm;
▶Resolution:20ppr,100ppr;
▶Supply Voltage:5v, 12v, 5-24v(+-10%)
▶Output form:Line Driver, Voltage Output
▶Emergency Button:N/A
▶Enable Button:N/A -

GT-1474 Series Manual Pluse Generator With Emergency Stop Button For CNC Lathe And Printing Mechanis
▶Size:134*68mm;
▶Resolution:20ppr,100ppr;
▶Supply Voltage:5v, 12v, 5-24v(+-10%)
▶Output form:Line Driver, Voltage Output
▶Emergency Stop Button:Yes
▶Enable Button:Yes -

GT-2188 Series Manual Pluse Generator With Emergency Stop Button For CNC Lathe And Printing Mechanis
▶Size:210*88mm
▶Resolution:25ppr,100ppr
▶Supply Voltage:5v, 12v, 5-24v(+-10%)
▶Output:Line Driver, Voltage Output
▶Emergency Stop Button:Yes
▶Enable Button:Yes -

GT-8060 Series Hand Wheel for CNC Lathe & Printing Mechanism – High Precision Manual Pulse Generator (MPG)
▶Size::80x60mm
▶Resolution::25ppr, 100ppr
▶Output::Line Driver, Voltage Output
▶Voltage::5v & 5-26v
▶Max.Rotary Speed::600rpm -

GT-6047 Hand Wheel for CNC Lathe and Printing Mechanism: Precision Pulse Generation and Reliable Performance
▶Size::60x47mm
▶Resolution::25ppr, 100ppr
▶Output::Line Driver, Voltage Output
▶Voltage::5v & 5-26v
▶Max.Rotary Speed::600rpm -
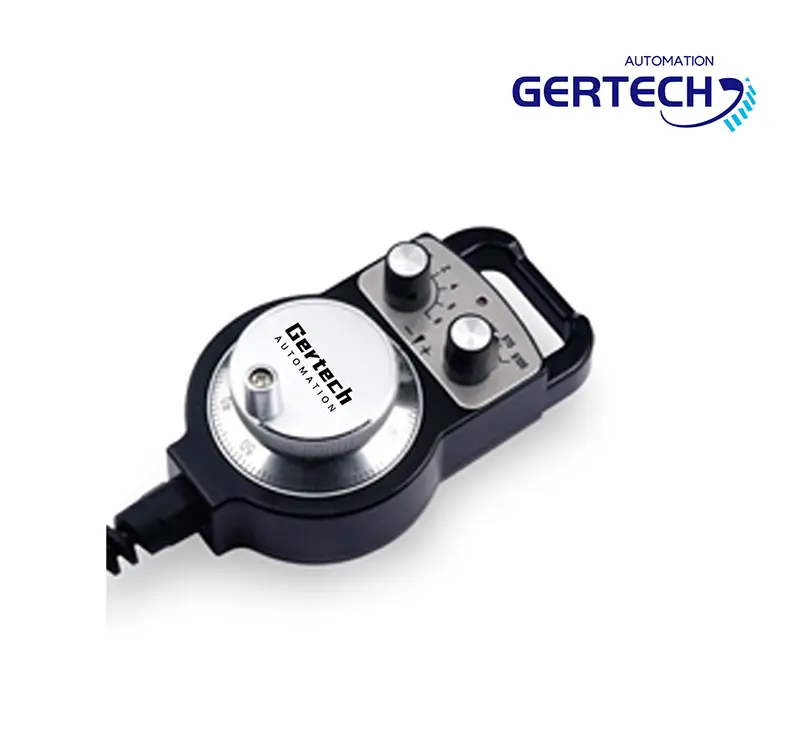

GT-1274 Series Manual Pluse Generator For CNC Lathe And Printing Mechanism
▶Size:122*74mm;
▶Resolution:20ppr,100ppr;
▶Supply Voltage:5v, 12v, 5-24v(+-10%)
▶Output form:Line Driver, Voltage Output
▶Emergency Button:N/A
▶Enable Button:N/A -

GT-1468 Series Manual Pluse Generator With Emergency Stop Button For CNC Lathe And Printing Mechanis
▶Size:134*68mm;
▶Resolution:20ppr,100ppr;
▶Supply Voltage:5v, 12v, 5-24v(+-10%)
▶Output form:Line Driver, Voltage Output
▶Emergency Button:Yes
▶Enable Button:Yes -

GT-1469 Series Manual Pluse Generator For CNC Lathe And Printing Mechanism
▶Size:134*68mm;
▶Resolution:20ppr,100ppr;
▶Supply Voltage:5v, 12v, 5-24v(+-10%)
▶Output form:Line Driver, Voltage Output
▶Emergency Button:N/A
▶Enable Button:N/A -

GT-1474 Series Manual Pluse Generator With Emergency Stop Button For CNC Lathe And Printing Mechanis
▶Size:134*68mm;
▶Resolution:20ppr,100ppr;
▶Supply Voltage:5v, 12v, 5-24v(+-10%)
▶Output form:Line Driver, Voltage Output
▶Emergency Stop Button:Yes
▶Enable Button:Yes -

GT-2188 Series Manual Pluse Generator With Emergency Stop Button For CNC Lathe And Printing Mechanis
▶Size:210*88mm
▶Resolution:25ppr,100ppr
▶Supply Voltage:5v, 12v, 5-24v(+-10%)
▶Output:Line Driver, Voltage Output
▶Emergency Stop Button:Yes
▶Enable Button:Yes -

GT-8060 Series Hand Wheel for CNC Lathe & Printing Mechanism – High Precision Manual Pulse Generator (MPG)
▶Size::80x60mm
▶Resolution::25ppr, 100ppr
▶Output::Line Driver, Voltage Output
▶Voltage::5v & 5-26v
▶Max.Rotary Speed::600rpm -

GT-6047 Hand Wheel for CNC Lathe and Printing Mechanism: Precision Pulse Generation and Reliable Performance
▶Size::60x47mm
▶Resolution::25ppr, 100ppr
▶Output::Line Driver, Voltage Output
▶Voltage::5v & 5-26v
▶Max.Rotary Speed::600rpm -

GT-1274 Series Manual Pluse Generator For CNC Lathe And Printing Mechanism
▶Size:122*74mm;
▶Resolution:20ppr,100ppr;
▶Supply Voltage:5v, 12v, 5-24v(+-10%)
▶Output form:Line Driver, Voltage Output
▶Emergency Button:N/A
▶Enable Button:N/A -

GT-1468 Series Manual Pluse Generator With Emergency Stop Button For CNC Lathe And Printing Mechanis
▶Size:134*68mm;
▶Resolution:20ppr,100ppr;
▶Supply Voltage:5v, 12v, 5-24v(+-10%)
▶Output form:Line Driver, Voltage Output
▶Emergency Button:Yes
▶Enable Button:Yes
-
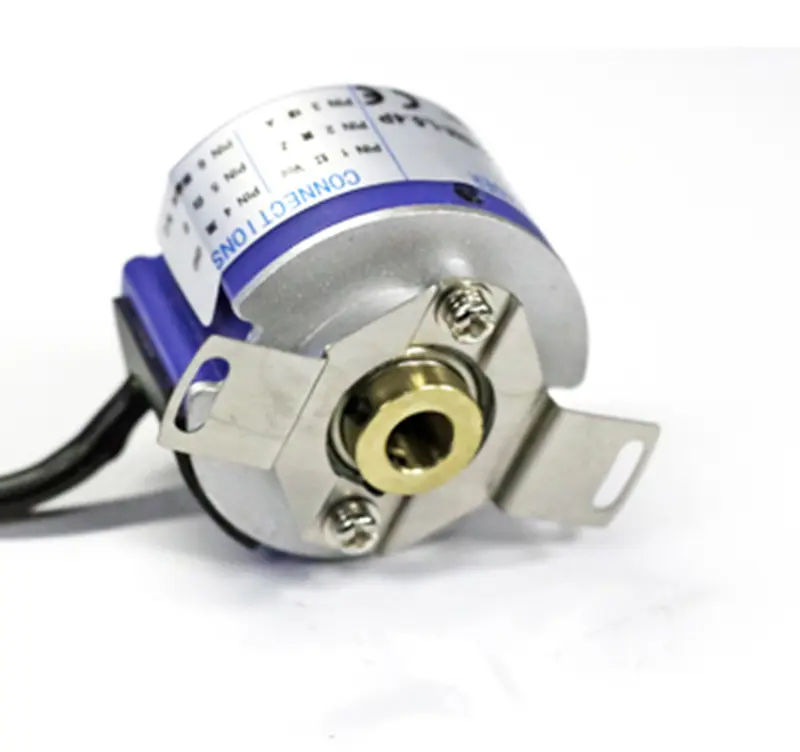

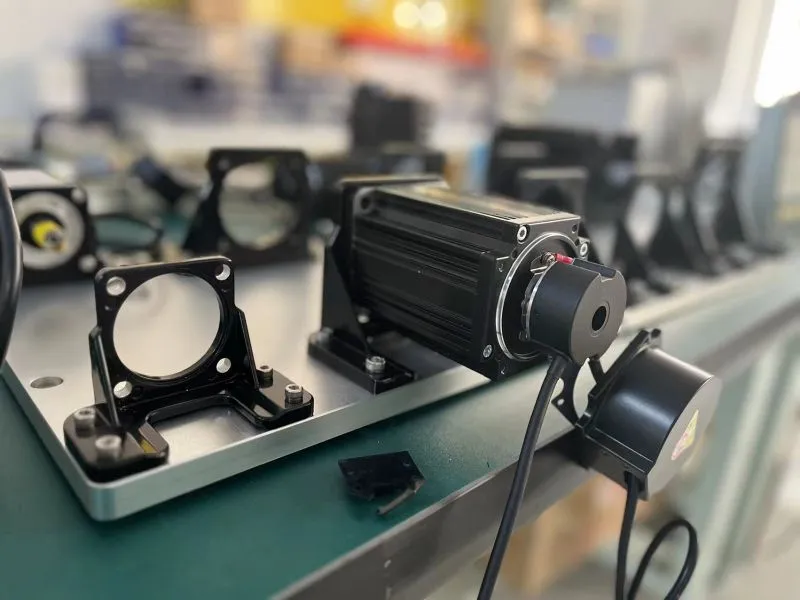
GS-SV35 Series Servo Motor Encoder
▶Housing Diameter:35mm;
▶Bole Diameter:5,6,8mm;
▶Resolution: 1000,1024,1250,2000,2048, 2500,4000,4096;ppr;
▶Supply Voltage:5v,8-29v; -

GS-SVZ48 Series Servo Motor Encoder
▶Housing Diameter:48mm;
▶Bole Diameter:09mm(Taper:1:10);
▶Resolution: 1000,1024,1250,2000,2048, 2500,4000,4096;ppr;
▶Supply Voltage:5v,8-29v; -

GS-SVZ35 Series Servo Motor Encoder
▶Housing Diameter:48mm;
▶Bole Diameter:6,8,10mm;
▶Resolution: 1000,1024,1250,2000,2048, 2500,4000,4096;ppr;
▶Supply Voltage:5v,8-29v; -

GS-SV35 Series Servo Motor Encoder
▶Housing Diameter:35mm;
▶Bole Diameter:5,6,8mm;
▶Resolution: 1000,1024,1250,2000,2048, 2500,4000,4096;ppr;
▶Supply Voltage:5v,8-29v; -

GS-SVZ48 Series Servo Motor Encoder
▶Housing Diameter:48mm;
▶Bole Diameter:09mm(Taper:1:10);
▶Resolution: 1000,1024,1250,2000,2048, 2500,4000,4096;ppr;
▶Supply Voltage:5v,8-29v; -

GS-SVZ35 Series Servo Motor Encoder
▶Housing Diameter:48mm;
▶Bole Diameter:6,8,10mm;
▶Resolution: 1000,1024,1250,2000,2048, 2500,4000,4096;ppr;
▶Supply Voltage:5v,8-29v; -

GS-SV35 Series Servo Motor Encoder
▶Housing Diameter:35mm;
▶Bole Diameter:5,6,8mm;
▶Resolution: 1000,1024,1250,2000,2048, 2500,4000,4096;ppr;
▶Supply Voltage:5v,8-29v; -

GS-SVZ48 Series Servo Motor Encoder
▶Housing Diameter:48mm;
▶Bole Diameter:09mm(Taper:1:10);
▶Resolution: 1000,1024,1250,2000,2048, 2500,4000,4096;ppr;
▶Supply Voltage:5v,8-29v; -

GS-SVZ35 Series Servo Motor Encoder
▶Housing Diameter:48mm;
▶Bole Diameter:6,8,10mm;
▶Resolution: 1000,1024,1250,2000,2048, 2500,4000,4096;ppr;
▶Supply Voltage:5v,8-29v;
our projects
Gertech Sensors are widely applied in the textile machinery, hoisting cranes, CNC machine, experimental machine and so on.
-

Wind Power Generation
-

Water Conservancy Project
-

Hoisting Machinery
-

CNC Machine Tool
-

Textile Machinery
-

Aeronautical and Space Industry
-

Who We Are
GERTECH is an technical enterprise Located in Weihai City ShanDong Province, China.
-

Main Products
Our Main Products: Industrial Rotary Encoder, Inductive Proximity Sensor, Capacitive Proximity Sensor etc.
-

our projects
Gertech Sensors are widely applied in the textile machinery, hoisting cranes, CNC machine, experimental machine and so on.